Introduction#
In this post I will show you how to migrate a traditional microservices architecture to an implementation with Spring Cloud. We’ll start from a functional system with three independent microservices (ms01producto, ms02reserva, ms03stock) and a React frontend, and evolve it into a more robust and scalable architecture using Spring Cloud components.
📚 Recommended reading: If you want to understand the theory behind Spring Cloud before seeing the practical implementation, I recommend reading Spring Cloud: Keys to Java Distributed Systems, where I explain the fundamentals and benefits of this technology.
📁 Project Repositories#
To follow this tutorial step by step, you can download the following repositories:
🚀 Base Project (Starting point): spring-cloud-microservices-base
Contains the initial microservices architecture without Spring Cloud✅ Final Project (Complete result): spring-cloud-microservices-final
The full implementation with all Spring Cloud components integrated
🎯 Implementation Challenge: It would be great if you use the base repository as a starting point and try to implement the entire migration to Spring Cloud on your own! Follow the steps in this tutorial as a guide and then compare your result with the final project. It’s an excellent way to consolidate learning and build practical skills.
⚠️ Important — Version Compatibility:
This tutorial uses Spring Cloud 2025.0.0 which is compatible with Spring Boot 3.5.x. This combination ensures maximum stability and support for the latest features. In allpom.xmlexamples you will finddependencyManagementconfigured correctly for this version.
🏗️ Initial Architecture: Before Spring Cloud#
Our starting point was a simple but functional architecture:
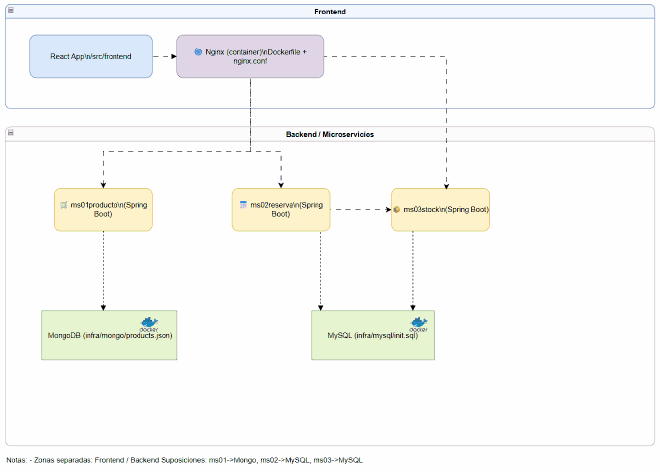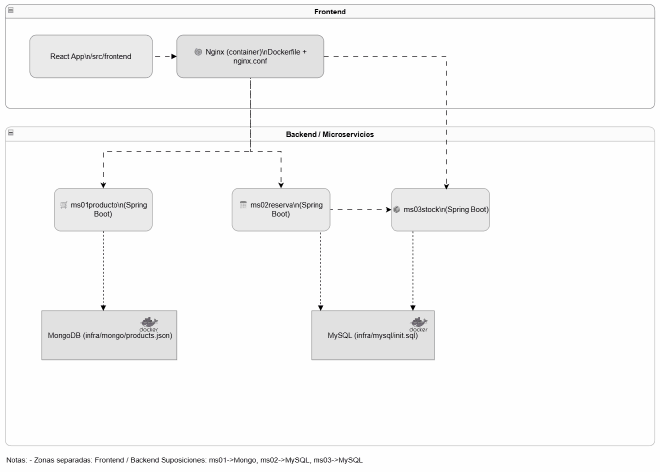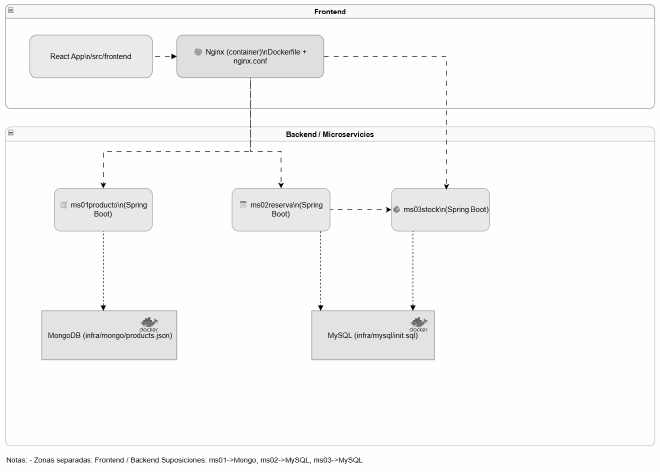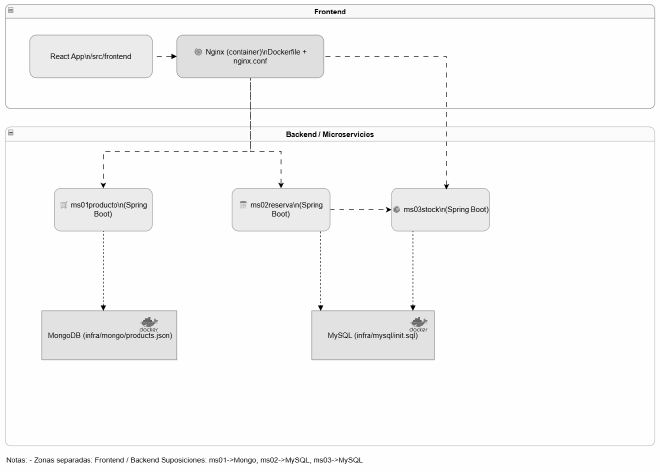
Original Architecture Characteristics#
- Direct communication: Services communicated through hardcoded URLs
- Distributed configuration: Each microservice had its own configuration
- No service discovery: URLs were configured manually
- Direct frontend: React connected directly to each microservice
- No single entry point: Multiple ports exposed to the client
Original Tech Stack#
# Microservices in place
ms01producto: # Port 8081 - MongoDB
ms02reserva: # Port 8080 - MySQL
ms03stock: # Port 8082 - MySQL
frontend: # Port 3000 - React + Nginx
🚀 Final Architecture: With Spring Cloud#
The evolved architecture includes all Spring Cloud components:
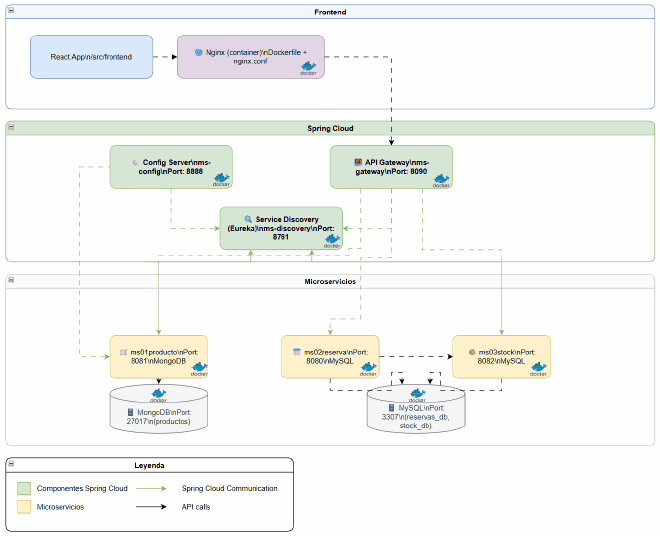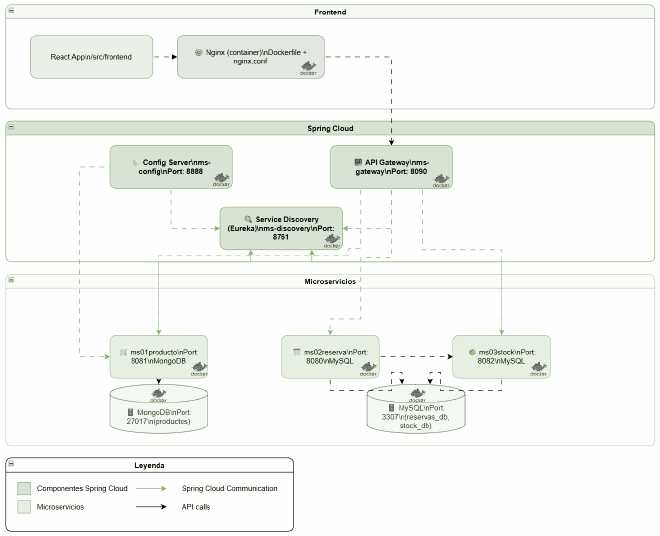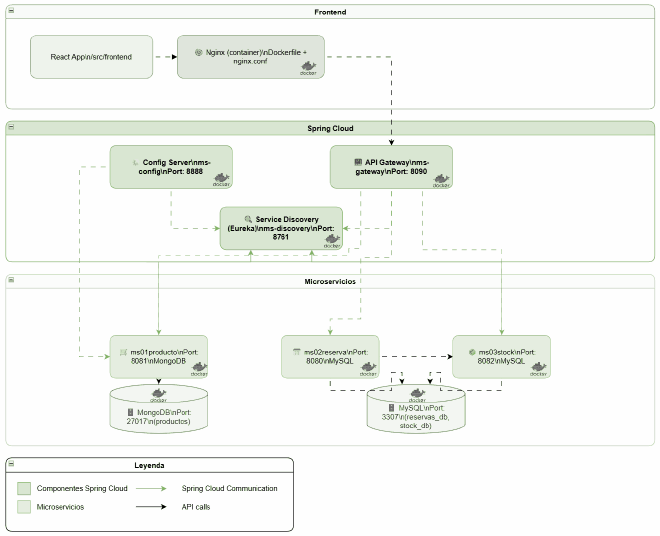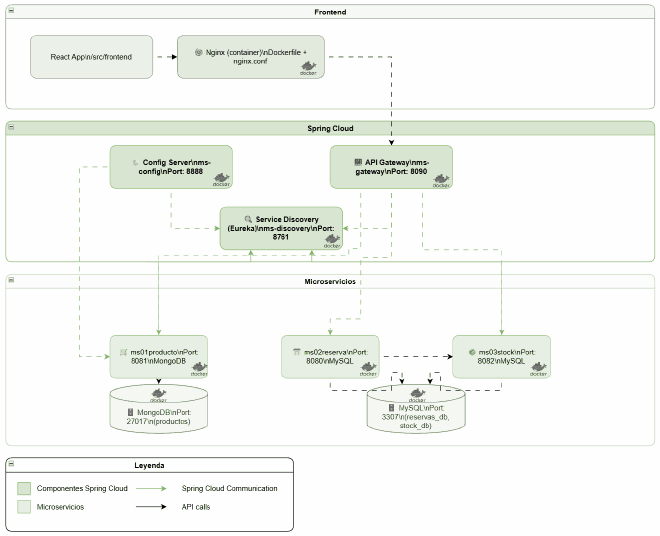
New Components Added#
- Config Server (Port 8888) — Centralized configuration
- Service Discovery (Port 8761) — Eureka Server
- API Gateway (Port 8090) — Single entry point
📋 Step by Step: Spring Cloud Implementation#
1. Config Server — Centralized Configuration#
First we create the centralized configuration server.
Create the ms-config project#
# Project structure
ms-config/
├── src/main/java/com/indra/ms_config/
│ └── MsConfigApplication.java
├── src/main/resources/
│ └── application.properties
├── config-repo/
│ └── ms01producto.properties
└── pom.xml
Dependencies in pom.xml#
<properties>
<java.version>21</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2025.0.0</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
Main class#
package com.indra.ms_config;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.EnableConfigServer;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigServer // Enables Config Server
public class MsConfigApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MsConfigApplication.class, args);
}
}
application.properties configuration#
spring.application.name=ms-config
server.port=8888
# Configuration for local files
spring.profiles.active=native
spring.cloud.config.server.native.search-locations=file:///config-repo
# Actuator endpoints
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
management.endpoint.health.show-details=always
Centralized configuration for ms01producto#
# config-repo/ms01producto.properties
spring.application.name=ms01producto
server.port=${SERVER_PORT:8081}
# MongoDB configuration
spring.data.mongodb.uri=${SPRING_DATA_MONGODB_URI:mongodb://localhost:27017/productos_db}
# Actuator configuration
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=health,info,metrics,prometheus
management.endpoint.health.show-details=always
management.info.env.enabled=true
2. Service Discovery — Eureka Server#
We implement the service discovery server.
Create the ms-discovery project#
# Project structure
ms-discovery/
├── src/main/java/com/indra/ms_discovery/
│ └── MsDiscoveryApplication.java
├── src/main/resources/
│ └── application.properties
└── pom.xml
Specific dependencies#
<properties>
<java.version>21</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2025.0.0</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
Main class#
package com.indra.ms_discovery;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer // Enables Eureka Server
public class MsDiscoveryApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MsDiscoveryApplication.class, args);
}
}
Eureka Server configuration#
spring.application.name=ms-discovery
server.port=8761
# Eureka Server configuration
eureka.client.register-with-eureka=false
eureka.client.fetch-registry=false
eureka.server.enable-self-preservation=false
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=${EUREKA_CLIENT_SERVICE_URL:http://localhost:8761/eureka/}
# Actuator
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
management.endpoint.health.show-details=always
3. API Gateway — Single Entry Point#
We create the gateway to centralize all requests.
Create the ms-gateway project#
# Project structure
ms-gateway/
├── src/main/java/com/indra/ms_gateway/
│ └── MsGatewayApplication.java
├── src/main/resources/
│ └── application.properties
└── pom.xml
Gateway dependencies#
<properties>
<java.version>21</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2025.0.0</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
Main class (Simple)#
package com.indra.ms_gateway;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class MsGatewayApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MsGatewayApplication.class, args);
}
}
Routes and CORS configuration#
spring.application.name=ms-gateway
server.port=8090
# Eureka client configuration
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=${EUREKA_CLIENT_SERVICE_URL:http://localhost:8761/eureka/}
eureka.instance.instance-id=${spring.application.name}:${spring.application.instance_id:${random.value}}
# Gateway Discovery Locator
spring.cloud.gateway.server.webflux.discovery.locator.enabled=true
spring.cloud.gateway.server.webflux.discovery.locator.lower-case-service-id=true
# CORS Configuration
spring.cloud.gateway.server.webflux.globalcors.add-to-simple-url-handler-mapping=true
spring.cloud.gateway.server.webflux.globalcors.cors-configurations.[/**].allowed-origins=http://localhost:3000
spring.cloud.gateway.server.webflux.globalcors.cors-configurations.[/**].allowed-methods=GET,POST,PUT,DELETE,OPTIONS,HEAD,PATCH
spring.cloud.gateway.server.webflux.globalcors.cors-configurations.[/**].allowed-headers=*
# Routes Configuration
spring.cloud.gateway.server.webflux.routes[0].id=ms01producto-routes
spring.cloud.gateway.server.webflux.routes[0].uri=lb://ms01producto
spring.cloud.gateway.server.webflux.routes[0].predicates[0]=Path=/ms01producto/**
spring.cloud.gateway.server.webflux.routes[0].filters[0]=StripPrefix=1
spring.cloud.gateway.server.webflux.routes[1].id=ms02reserva-routes
spring.cloud.gateway.server.webflux.routes[1].uri=lb://ms02reserva
spring.cloud.gateway.server.webflux.routes[1].predicates[0]=Path=/ms02reserva/**
spring.cloud.gateway.server.webflux.routes[1].filters[0]=StripPrefix=1
spring.cloud.gateway.server.webflux.routes[2].id=ms03stock-routes
spring.cloud.gateway.server.webflux.routes[2].uri=lb://ms03stock
spring.cloud.gateway.server.webflux.routes[2].predicates[0]=Path=/ms03stock/**
spring.cloud.gateway.server.webflux.routes[2].filters[0]=StripPrefix=1
4. Changes to Existing Microservices#
Add Spring Cloud dependencies#
In each microservice (ms01producto, ms02reserva, ms03stock):
<!-- Add to pom.xml -->
<properties>
<java.version>21</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2025.0.0</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<!-- Add these dependencies -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bootstrap</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Add dependency management -->
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
💡 Note about spring-cloud-starter-bootstrap:
This dependency is mandatory in Spring Boot 3.x forbootstrap.propertiesto work. Without it, Spring Cloud Config will not load the configuration before the application context, causing connection errors to the Config Server.
Enable Discovery Client#
// In ms01producto/src/main/java/com/indra/Ms01productoApplication.java
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient // Add this annotation
public class Ms01productoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Ms01productoApplication.class, args);
}
}
Configure bootstrap.properties#
📝 Important: In Spring Boot 3.x, to use
bootstrap.propertiesyou must add thespring-cloud-starter-bootstrapdependency included above. Without this dependency, thebootstrap.propertiesfile will be ignored.
# ms01producto/src/main/resources/bootstrap.properties
spring.application.name=ms01producto
spring.cloud.config.uri=${SPRING_CLOUD_CONFIG_URI:http://localhost:8888}
# Config Server retry configuration
spring.cloud.config.fail-fast=true
spring.cloud.config.retry.initial-interval=1500
spring.cloud.config.retry.max-interval=10000
spring.cloud.config.retry.max-attempts=10
# Eureka client configuration
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=${EUREKA_CLIENT_SERVICE_URL:http://localhost:8761/eureka/}
eureka.instance.instance-id=${spring.application.name}:${spring.application.instance_id:${random.value}}
Update Inter-service Communication#
// In ms02reserva - InventoryClientService
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class InventoryClientService {
private final RestTemplate restTemplate;
private final DiscoveryClient discoveryClient; // DiscoveryClient injection
@Value("${stock.service.url:http://ms03stock:8082}")
private String stockServiceUrl;
public Boolean stockAvailable(String code) {
// Use Service Discovery
ServiceInstance instance = discoveryClient.getInstances("MS03STOCK")
.stream().findFirst().orElse(null);
String url = instance.getUri() + "/api/stock/" + code;
RestTemplate directRestTemplate = new RestTemplate();
return directRestTemplate.getForObject(url, Boolean.class);
}
}
5. Docker Compose Update#
Generation with docker init#
First we use docker init to generate the base Dockerfiles:
# For each microservice
cd ms-config && docker init
cd ../ms-discovery && docker init
cd ../ms-gateway && docker init
cd ../ms01producto && docker init
cd ../ms02reserva && docker init
cd ../ms03stock && docker init
Final Docker Compose#
services:
# Databases (unchanged)
mysql:
image: mysql:8.0
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: rootpass
MYSQL_USER: user
MYSQL_PASSWORD: pass
ports:
- "3307:3306"
volumes:
- mysql-data:/var/lib/mysql
- ./infra/mysql/init.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/init.sql:ro
mongo:
image: mongo:6.0
ports:
- "27017:27017"
volumes:
- mongo-data:/data/db
- ./infra/mongo/products.json:/data/products.json:ro
- ./infra/mongo/mongo-init.sh:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/mongo-init.sh:ro
command: ["bash", "/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/mongo-init.sh"]
# Spring Cloud Components
ms-config:
build:
context: ./ms-config
environment:
- SPRING_CLOUD_CONFIG_SERVER_NATIVE_SEARCH_LOCATIONS=file:///config-repo
volumes:
- ./ms-config/config-repo:/config-repo:ro
ports:
- 8888:8888
ms-discovery:
build:
context: ./ms-discovery
environment:
- EUREKA_CLIENT_SERVICE_URL=http://ms-discovery:8761/eureka/
ports:
- 8761:8761
ms-gateway:
build:
context: ./ms-gateway
environment:
- EUREKA_CLIENT_SERVICE_URL=http://ms-discovery:8761/eureka/
ports:
- 8090:8090
depends_on:
- ms-config
- ms-discovery
- ms01producto
- ms02reserva
- ms03stock
# Updated microservices
ms01producto:
build:
context: ./ms01producto
environment:
- SPRING_CLOUD_CONFIG_URI=http://ms-config:8888
- EUREKA_CLIENT_SERVICE_URL=http://ms-discovery:8761/eureka/
- SPRING_DATA_MONGODB_URI=mongodb://mongo:27017/productos_db
ports:
- 8081:8081
depends_on:
- ms-config
- ms-discovery
- mongo
ms02reserva:
build:
context: ./ms02reserva
environment:
- EUREKA_CLIENT_SERVICE_URL=http://ms-discovery:8761/eureka/
- SPRING_DATASOURCE_URL=jdbc:mysql://mysql:3306/reservas_db?useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true
- SPRING_DATASOURCE_USERNAME=user
- SPRING_DATASOURCE_PASSWORD=pass
- STOCK_SERVICE_URL=http://ms03stock:8082
ports:
- 8080:8080
depends_on:
- ms-config
- ms-discovery
- mysql
ms03stock:
build:
context: ./ms03stock
environment:
- EUREKA_CLIENT_SERVICE_URL=http://ms-discovery:8761/eureka/
- SPRING_DATASOURCE_URL=jdbc:mysql://mysql:3306/stock_db?useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true
- SPRING_DATASOURCE_USERNAME=user
- SPRING_DATASOURCE_PASSWORD=pass
ports:
- 8082:8082
depends_on:
- ms-config
- ms-discovery
- mysql
# Frontend (no significant changes)
frontend:
build:
context: ./frontend
ports:
- 3000:80
depends_on:
- ms-gateway
volumes:
mysql-data:
mongo-data:
🔄 Comparison: Before vs After#
Service Communication#
Before:
// Frontend connecting directly
const API_URLS = {
productos: 'http://localhost:8081/api/productos',
reservas: 'http://localhost:8080/api/reservas',
stock: 'http://localhost:8082/api/stock'
};
After:
// Frontend using API Gateway
const API_BASE = 'http://localhost:8090';
const API_URLS = {
productos: `${API_BASE}/ms01producto/api/productos`,
reservas: `${API_BASE}/ms02reserva/api/reservas`,
stock: `${API_BASE}/ms03stock/api/stock`
};
🚀 Run Commands#
Local Development#
# 1. Start databases
docker compose up mysql mongo -d
# 2. Start Spring Cloud components (in order)
./mvnw spring-boot:run -f ms-config/pom.xml
./mvnw spring-boot:run -f ms-discovery/pom.xml
./mvnw spring-boot:run -f ms-gateway/pom.xml
# 3. Start microservices
./mvnw spring-boot:run -f ms01producto/pom.xml
./mvnw spring-boot:run -f ms02reserva/pom.xml
./mvnw spring-boot:run -f ms03stock/pom.xml
# 4. Start frontend
cd frontend && npm start
Production with Docker#
# All-in-one
docker compose up --build -d
# Verify services
docker compose ps
docker compose logs ms-discovery # Eureka logs
📊 Benefits Achieved#
1. Centralized Configuration#
- ✅ A single place to configure all services
- ✅ Hot updates without restarts
- ✅ Per-environment configurations (dev, prod)
2. Service Discovery#
- ✅ Auto-registration of services
- ✅ Automatic load balancing
- ✅ Built-in health checking
3. API Gateway#
- ✅ Single entry point for clients
- ✅ Dynamic routing based on services
- ✅ Centralized CORS
- ✅ Option to add authentication/authorization
4. Monitoring and Observability#
- ✅ Actuator endpoints across services
- ✅ Eureka dashboard to view service status
- ✅ Centralized metrics
🔍 Access URLs#
Admin Interfaces#
- Eureka Dashboard: http://localhost:8761
- Config Server: http://localhost:8888/ms01producto/default
- Gateway Health: http://localhost:8090/actuator/health
APIs (via Gateway)#
- Productos: http://localhost:8090/ms01producto/api/productos
- Reservas: http://localhost:8090/ms02reserva/api/reservas
- Stock: http://localhost:8090/ms03stock/api/stock
Frontend#
- React App: http://localhost:3000
🎯 Next Steps#
This implementation lays the foundation to add:
- Circuit Breakers with Resilience4j
- Distributed Tracing with Sleuth/Zipkin
- Security with Spring Security OAuth2
- Metrics with Micrometer/Prometheus
- Distributed caching with Redis
📝 Conclusion#
Migrating from a traditional microservices architecture to Spring Cloud brings significant benefits in terms of:
- Maintainability: centralized configuration
- Scalability: automatic discovery and load balancing
- Observability: built-in monitoring
- Resilience: foundation for circuit breakers and retry policies
While the process requires some initial investment, it provides a solid foundation for the system’s long-term growth and evolution.
This post documents the complete evolution of our Doggie Inn Pet Shop Management System towards a modern architecture with Spring Cloud.
